Ambisonic BRIR
The Ambisonic BRIR Convolution Module of the Binaural Rendering Toolbox enables the spatial audio rendering of multiple sound sources in an ambisonic environment. By leveraging the convolution with Binaural Room Impulse Responses (BRIR) in the ambisonic domain, this module processes the input sources considering their positions and the listener's position and orientation. It supports ambisonic encoding of orders 1, 2, or 3, and uses to decode virtual loudspeakers located at the vertices of regular polyhedra (octahedron for first-order, icosahedron for second-order, and dodecahedron for third-order).
In order to optimize the process, the module convolves the ambisonic signal directly with the ambisonic mix of the virtual loudspeakers' impulse responses, subsequently mixing all right and left channels separately, as it's shown in the diagram shown below. Uniformly partitioned convolution is used to compute the convolution in the frequency domain.
The diagram below illustrates the key components of the system and how they work together. From handling input parameters to generating and processing ambisonic signals, the system employs ambisonics and convolution techniques to accurately simulate 3D audio environments. The components and their respective functionalities are detailed below.
- Input Handling: The module accepts a set of audio sources along with their positions in space, as well as the position and orientation of the listener.
- Ambisonic Encoding: The relative positions of each source with respect to the listener are used to encode the sources into an ambisonic format of the specified order (1st, 2nd, or 3rd).
- Virtual Loudspeaker: Impulse responses are got from the BRIR file for those positions of teh virtual loudspeakers, arranged at the vertices of a regular polyhedron corresponding to the ambisonic order.
- Convolution: Rather than convolving each virtual loudspeaker signal with the HRIR individually, the module convolves the ambisonic signal directly with the ambisonic mix of the BRIRs for the virtual loudspeakers.
- Channel Mixing: The convoluted signals are mixed into separate left and right channels, resulting in the final binaural audio output.
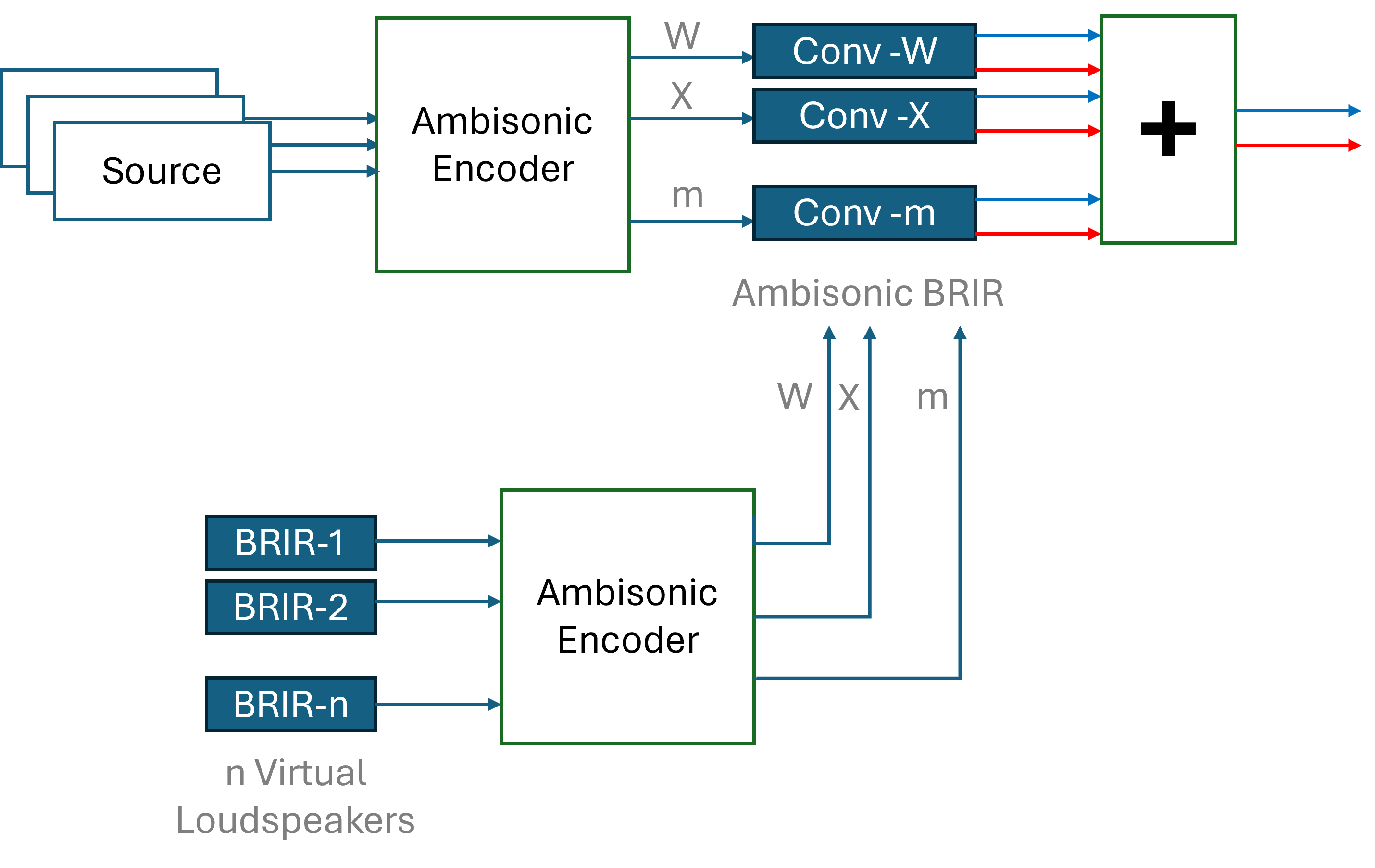
Ambisonic BRIR model diagram.
Functional Overview
To properly load and configure a file using this class, the process must begin with the Begin Setup method, which initializes the system with a specified ambisonic order and normalization scheme. This step sets up the necessary parameters for subsequent operations. Once all required configurations and impulse responses have been added, the setup process is finalized using the End Setup method. This ensures that the class is ready for use, as indicated by the IsReady method, which verifies if the Ambisonic BIR is loaded and operational. During the setup, additional methods can be used to enhance the configuration. For instance, Add Impulse Response allows adding a new impulse response associated with a specific channel and listener position. Finally, the system provides methods for retrieving configuration details, such as Get Channel Partitioned IR, which fetches the partitioned impulse response for a given channel and ear, taking into account the listener's current position and orientation.
Configuration Options
The methods provided by this service are as follows.
- Begin Setup: Initializes the setup process with the specified parameters.
- End Setup: Completes the setup process and confirms the system is ready.
- Reset: Resets the system to its initial state.
- Is Ready: Checks if the system is ready and the BRIR is loaded.
- Add Impulse Response: Adds a new impulse response associated with a specific channel and listener position.
- Get Channel Partitioned IR: Retrieves the partitioned impulse response for a channel and a specific ear, considering the listener's position and orientation.
- Add Impulse Responses From HRIR: Adds multiple impulse responses from a shared HRIR resource.
BRIR Format
A BRIR (Binaural Room Impulse Response) must be loaded. Readers can be used to load BRIR SOFA files. Depending on the Ambisonic order, the direction of the virtual loudspeakers are searched in the BRIR file. If some of them is not found, an interpolation among the three closest directions is performed. If different listener positions are provided, a different set of virtual loudspeakers will be created for every listener position. When rendering, the one with the closest position to the listener is selected to convolve. To determine if two positions are the same, a resolution of 1 meter is used.
Depending on how the BRIR is captured, several cases may be considered
-
One fixed listener with several source positions around it
-
One listener position with different orientations and one fixed source
-
Different listener positions with sources around