Ambisonic Domain Convolver Processor
The Ambisonic Domain Convolver Processor is a system designed for processing Ambisonic audio channels, performing frequency-domain transformations, convolutions, and mixing to produce spatially accurate sound for binaural listening. The processor handles multiple input channels and applies several processing stages, including FFT, convolution with Ambisonic BIR, and final mixing to create the output for the listener's ears.
Architecture
The internal block diagram of this class is as follows:
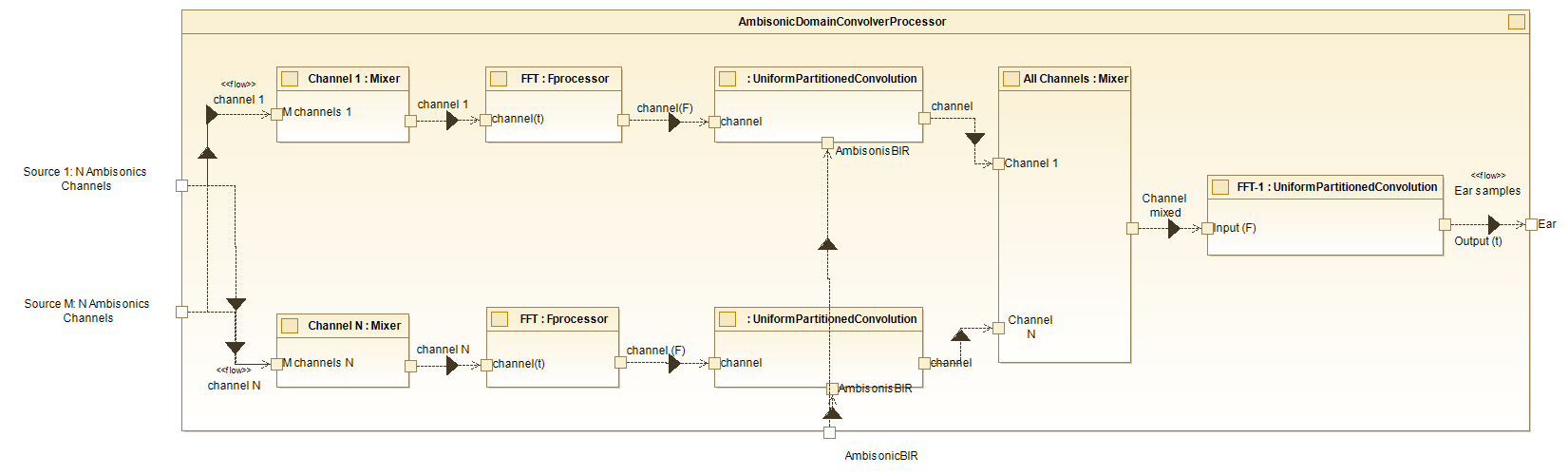
Ambisonic Domain Convolver Processor - Internal diagram.
As it is shown in the diagram, the Ambisonic Domain Convolver Processor takes multiple Ambisonic channels, applies FFT processing, convolves with Ambisonic BIR to create spatial effects, mixes the processed channels, and delivers the final output as binaural ear samples, simulating an immersive listening experience for the listener.
Key Components and Flow:
-
Channel Mixer: Each mixer processes the respective channels (
channel 1throughchannel N) from each sound source, for further frequency-domain transformation. -
FFT Processor: The FFT Processor blocks apply a Fast Fourier Transform. Each processed channel goes to Uniform Partitioned Convolution.
-
Uniform Partitioned Convolution: The frequency-domain channels are passed into the Uniform Partitioned Convolution blocks. These blocks convolve the signals with the AmbisonicBIR.
-
All Channels - Mixer: The convolved outputs from all channels (
Channel 1throughChannel N) are combined in the All Channels - Mixer. This step ensures the final output integrates contributions from all Ambisonic channels. -
Final Convolution and Output: The mixed signal (
Channel mixed) undergoes a final convolution step in the FFT : UniformPartitionedConvolution block. The result is output as Ear samples, simulating spatial audio perception at the listener's ears.